The Heart of Irrigation: Understanding the Yanma Pump
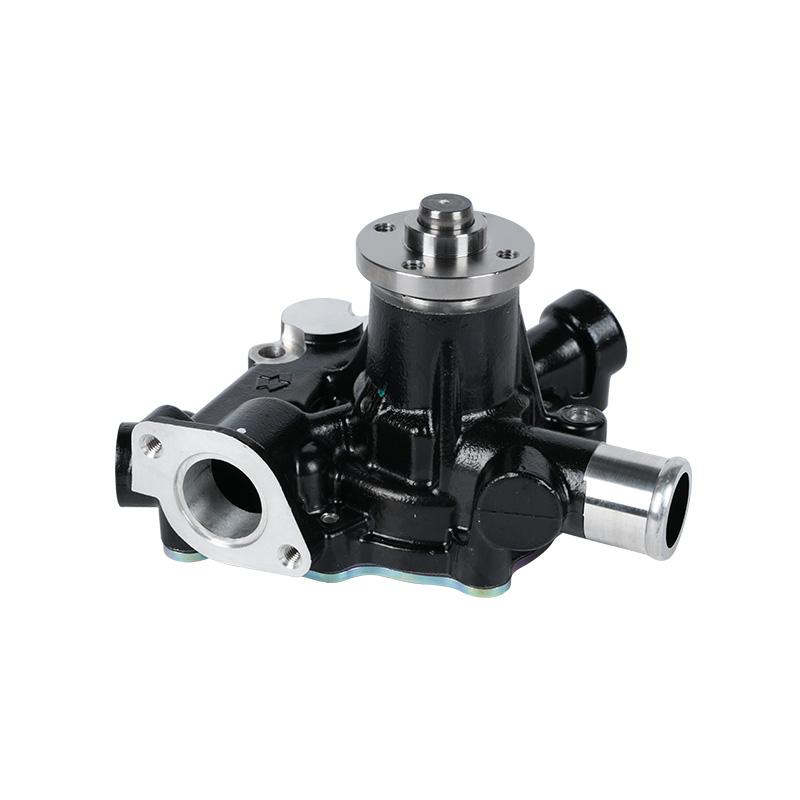

A Yanma pump represents a specific category of engine-driven water pump, commonly powered by Yanmar diesel engines, designed for demanding fluid transfer applications. This setup typically integrates a reliable Yanmar engine with a robust centrifugal pump unit, creating a self-contained, portable system for moving large volumes of water. The primary function of a Yanma pump is to provide high-flow, dependable water transfer in scenarios where electrical grid power is unavailable or impractical. It is a familiar sight in agriculture for field irrigation and drainage, in construction for dewatering excavations, and in emergency response for flood control. The combination of Yanmar's diesel engineering with a purpose-built pump assembly results in a tool valued for its durability and performance in tough conditions. This exploration outlines the typical configuration, operational principles, and common uses of a Yanma pump, concluding with its established role as a mobile and powerful solution for water management challenges.
The standard Yanma pump configuration consists of two main assemblies: the power source and the pumping mechanism. The power unit is typically a Yanmar air-cooled diesel engine, known for its fuel efficiency and longevity. This engine is directly coupled to the pump shaft, often via a flexible coupling to accommodate minor misalignment and absorb shock. The pump itself is usually a centrifugal design. In this type of Yanma pump, the engine spins an impeller inside a volute casing. As the impeller rotates, it imparts kinetic energy to the water, which is then converted to pressure as the flow is constrained by the casing's outward spiral shape. This design is effective for handling relatively clean water with suspended solids, making a Yanma pump suitable for the silty or debris-laden water often encountered in field and construction work.
Key performance specifications for a Yanma pump include flow rate, total head, and suction lift. The flow rate, measured in liters per minute or gallons per minute, indicates the volume of water the Yanma pump can move. Total head represents the maximum height the pump can push water vertically, accounting for both lift and friction losses in the hose. Suction lift is the vertical distance the pump can pull water up from the source to its inlet; a self-priming Yanma pump is designed to evacuate air from the suction hose and create a vacuum to draw water effectively, a critical feature for quick setup. The engine's horsepower rating determines the overall power available to drive the Yanma pump, influencing these performance parameters.
The operational utility of a Yanma pump is demonstrated across several sectors. In agriculture, it is indispensable for moving water from canals or reservoirs to fields, or for draining flooded areas. On construction sites, a Yanma pump is deployed to keep foundations and trenches dry. For municipal and disaster management teams, these pumps are used to manage stormwater, control flooding, and empty containment ponds. The portability of a Yanma pump, often mounted on a wheeled frame or skid, allows it to be moved to the point of need quickly. Its reliance on diesel fuel means it can operate independently for extended periods, given an adequate fuel supply, which is a significant advantage in remote locations.
Proper setup and maintenance are essential for reliable operation. Ensuring the suction hose is airtight and submerged, and that the discharge hose is secure, prevents loss of prime and inefficiency.
The Yanma pump embodies a practical and powerful approach to mobile water transfer. By pairing a dependable diesel engine with an efficient centrifugal pump, it creates a standalone system capable of tackling significant hydraulic tasks. Its design prioritizes mechanical simplicity, durability, and ease of deployment in field conditions. Therefore, for professionals in farming, construction, and civil works, a well-maintained Yanma pump is a critical asset, providing the hydraulic muscle needed to manage water effectively. Its persistent use in challenging environments underscores the value of its robust, engine-driven design, proving that for many high-volume, off-grid pumping needs, the integrated reliability of a Yanma pump remains a preferred and effective solution. The steady operation of a Yanma pump continues to support essential water movement tasks wherever they are required.