Understanding the Workflow in a Plastic Injection Mould Facility
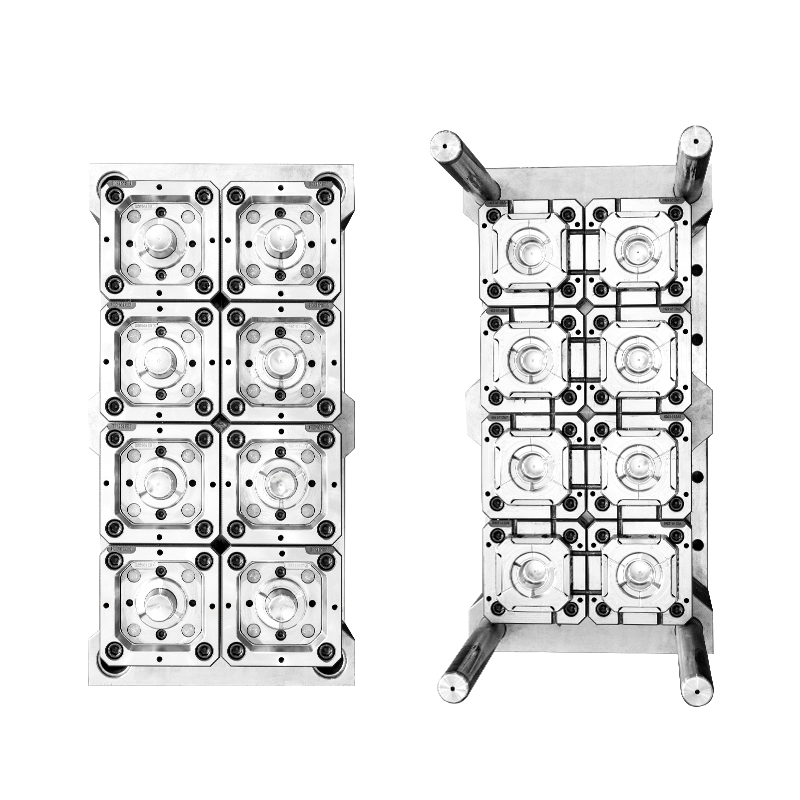
The capabilities of a contemporary plastic injection mould factory extend far beyond basic machining, encompassing a suite of advanced engineering services and specialized technologies. A key differentiator is the factory's proficiency in various mould technologies. This includes expertise in standard two-plate moulds, more complex three-plate moulds for automated part separation, and intricate family moulds that produce multiple different components in a single cycle. Furthermore, an advanced plastic injection mould factory will have extensive experience designing and integrating hot runner systems. These systems maintain the plastic in a molten state within the mould, eliminating material waste from cold runners and allowing for more complex gating, which improves part quality and reduces cycle times.
Handling projects with high complexity is a hallmark of a proficient plastic injection mould factory. This involves designing and building moulds with sophisticated actions like hydraulic or mechanical slides, lifters, and unscrewing mechanisms to form undercuts, internal threads, and complex geometries. The factory's engineering team must devise robust mechanical solutions within the mould structure to create these features and ensure they reliably retract before part ejection. Material science knowledge is also essential. Engineers at the plastic injection mould factory must select the appropriate grade of tool steel—such as P20, H13, or stainless steel—based on the plastic resin to be used, the expected production volume, and the required surface finish. For high-gloss parts, like automotive lenses or consumer electronics housings, the factory's polishing technicians must achieve a mirror-like finish on the steel surfaces, a skill that significantly impacts the final product's appearance and perceived quality.
To remain competitive, a forward-looking plastic injection mould factory invests in continuous technological advancement. This includes utilizing advanced mould flow analysis software to simulate how plastic will fill and cool within the mould cavity, predicting and preventing potential defects like air traps or weld lines before manufacturing begins. The adoption of additive manufacturing, or 3D printing, allows for the creation of conformal cooling channels. These channels follow the contour of the mould cavity more closely than traditional drilled lines, enabling vastly improved cooling efficiency, which reduces cycle times and minimizes part warpage. Many factories also offer value-added services such as product design for manufacturability consultations, helping clients optimize their part designs for the injection moulding process before the mould design is finalized. By integrating these advanced capabilities, a plastic injection mould factory positions itself not merely as a tool maker, but as a comprehensive engineering partner capable of solving complex manufacturing challenges and delivering a mould that ensures efficient, high-quality production.
- Art
- Causes
- Crafts
- Dance
- Drinks
- Film
- Fitness
- Food
- Jocuri
- Gardening
- Health
- Home
- Literature
- Music
- Networking
- Alte
- Party
- Religion
- Shopping
- Sports
- Theater
- Wellness


