Science of Thermal Control Used by Marine Insulation Firms
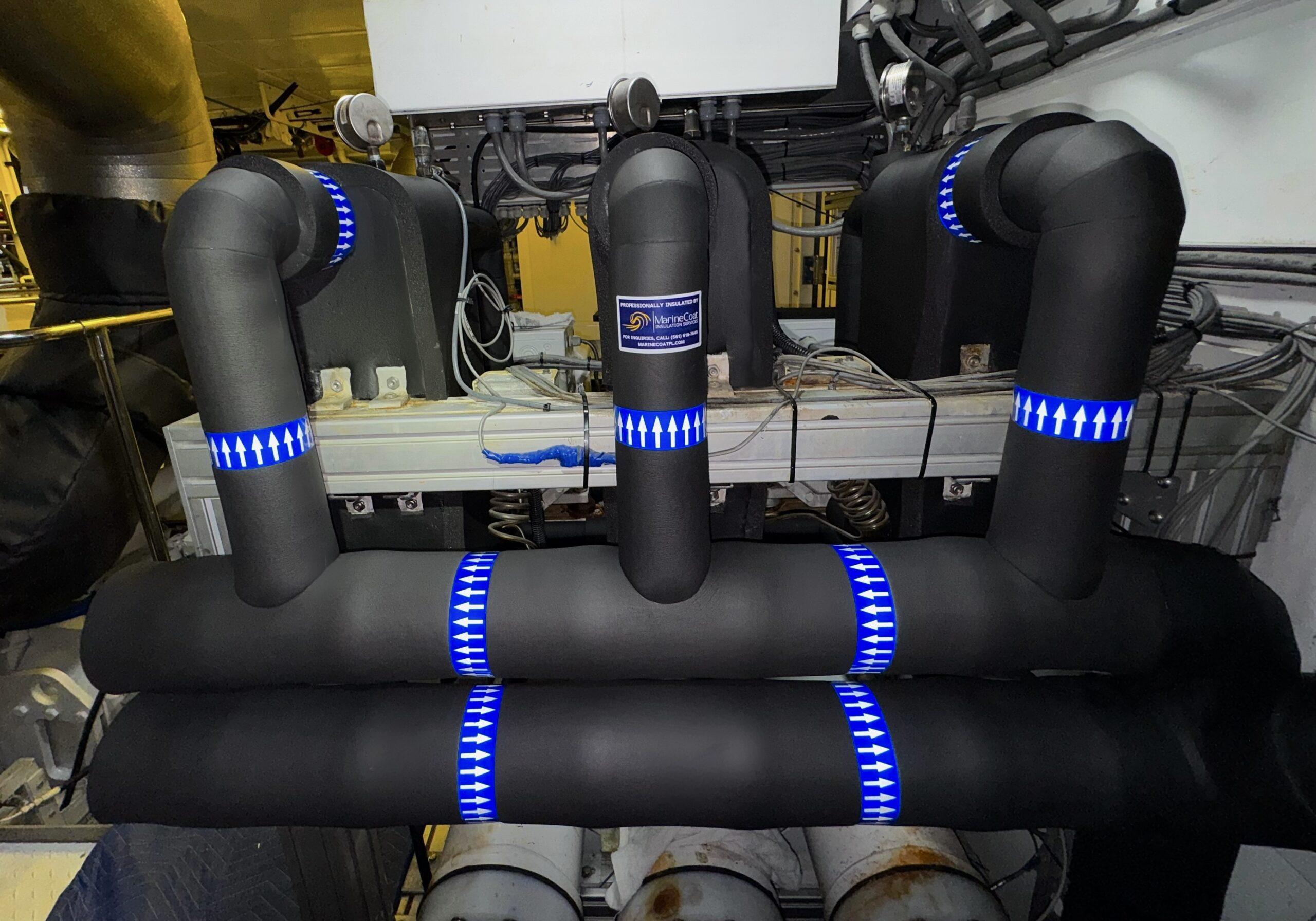
Thermal regulation within maritime environments is governed by complex scientific principles that extend far beyond basic heat containment. In the earliest phases of vessel engineering, marine insulation companies apply physics-based methodologies to manage energy transfer across shipboard systems. Through calculated use of marine pipe insulation, heat flow is controlled to protect equipment, stabilize operations, and safeguard crew members from hazardous exposure.
Thermal control is not merely an efficiency measure; it is a safety-driven discipline shaped by conduction, convection, and radiation dynamics. Within marine applications, insulation transforms these forces into manageable variables.
Fundamental Heat Transfer Principles in Marine Systems
Marine vessels host diverse thermal zones, from cryogenic pipelines to high-temperature exhaust conduits. Heat migrates through conduction along metallic surfaces, convection via air movement, and radiation from exposed components. Marine insulation companies design insulation systems that interrupt these transfer paths using scientifically selected materials.
Marine pipe insulation functions as a thermal resistor, lowering heat flux and preventing temperature escalation in surrounding compartments. This controlled resistance is essential for maintaining operational equilibrium within confined mechanical spaces.
Material Science and Thermal Resistance Engineering
Low Conductivity Fiber Structures
Insulation materials used at sea often rely on fibrous microstructures that entrap air pockets. These voids restrict molecular movement, diminishing conductive heat transfer. Marine insulation companies favor engineered mineral fibers and synthetic blends that maintain low thermal conductivity even under compressive stress.
Closed-Cell Thermal Barriers
Closed-cell compositions prevent convective heat movement by isolating gas molecules within sealed chambers. When applied as marine pipe insulation, these materials limit both heat transmission and moisture ingress, preserving insulation integrity in humid marine atmospheres.
Reflective and Radiant Control Layers
Radiant heat presents a significant challenge near engines and exhaust systems. Reflective foils integrated into insulation assemblies redirect infrared energy away from occupied spaces. This scientific approach enhances thermal control without increasing insulation thickness.
Thermodynamics in Engine Rooms and Process Areas
Engine rooms represent concentrated heat generation zones where thermal gradients fluctuate continuously. Marine insulation companies analyze these gradients to determine insulation density, thickness, and layering strategy. The goal is to equalize temperature differentials and prevent localized overheating.
Marine pipe insulation moderates surface temperatures, reducing radiant heat accumulation and stabilizing ambient conditions. This thermal equilibrium supports equipment longevity and improves crew working conditions.
Moisture Interaction and Vapor Diffusion Control
Thermal science in marine environments must also address phase change phenomena. When warm air contacts cooler surfaces, condensation forms. Marine insulation companies counter this through vapor diffusion control, using impermeable barriers that block moisture migration.
Properly engineered marine pipe insulation maintains surface temperatures above dew point thresholds, eliminating condensation formation. This scientific control mechanism directly reduces corrosion risk beneath insulation layers.
Fire Behavior and Heat Delay Science
Fire protection relies heavily on thermal delay principles. Insulation materials are selected for their ability to absorb and dissipate heat energy slowly. Marine insulation companies apply non-combustible insulation that prolongs structural integrity during fire exposure.
By limiting rapid temperature escalation, marine pipe insulation grants additional response time during emergencies. This delay can prevent fire spread between compartments, a critical safety requirement in maritime design.
Acoustic Energy and Thermal Correlation
Sound and heat energy often coexist within machinery spaces. Dense insulation materials attenuate sound waves while simultaneously restricting thermal transmission. Marine insulation companies exploit this dual-functionality to enhance habitability and compliance with occupational noise standards.
Marine pipe insulation contributes to vibration dampening, reducing mechanical energy transfer that could otherwise convert into unwanted heat through frictional processes.
Computational Modeling and Predictive Analysis
Modern insulation design increasingly relies on computational thermal modeling. Marine insulation companies utilize simulations to predict heat flow behavior under operational loads. These models guide material selection and installation geometry.
Predictive analysis ensures marine pipe insulation performs as intended across varying operating scenarios, from idle conditions to maximum propulsion output.
Sustainability and Thermal Efficiency Optimization
Thermal control also intersects with environmental stewardship. Efficient insulation reduces fuel consumption by minimizing energy loss. Marine insulation companies adopt materials that maintain thermal performance over extended service periods, reducing replacement frequency.
Long-lasting marine pipe insulation contributes to lower emissions and aligns with evolving sustainability objectives within the maritime sector.
Lifecycle Performance and System Stability
Thermal insulation must perform consistently throughout a vessel’s lifespan. Degradation alters thermal resistance and compromises safety. Marine insulation companies design systems that retain structural and thermal properties despite vibration, humidity, and temperature cycling.
Routine assessment of marine pipe insulation ensures thermal control remains effective, preserving compliance and operational reliability.
Conclusion: Science-Driven Thermal Mastery at Sea
Thermal control within marine environments is rooted in applied physics, material science, and engineering precision. By harnessing these principles, marine insulation companies deliver solutions that regulate heat, prevent hazards, and optimize vessel performance. When scientifically engineered and properly maintained, marine pipe insulation becomes a vital instrument for safety, efficiency, and long-term maritime resilience.
- Art
- Causes
- Crafts
- Dance
- Drinks
- Film
- Fitness
- Food
- Spiele
- Gardening
- Health
- Home
- Literature
- Music
- Networking
- Other
- Party
- Religion
- Shopping
- Sports
- Theater
- Wellness


