Real-Time Health and Performance Analytics for Capacitor Banks
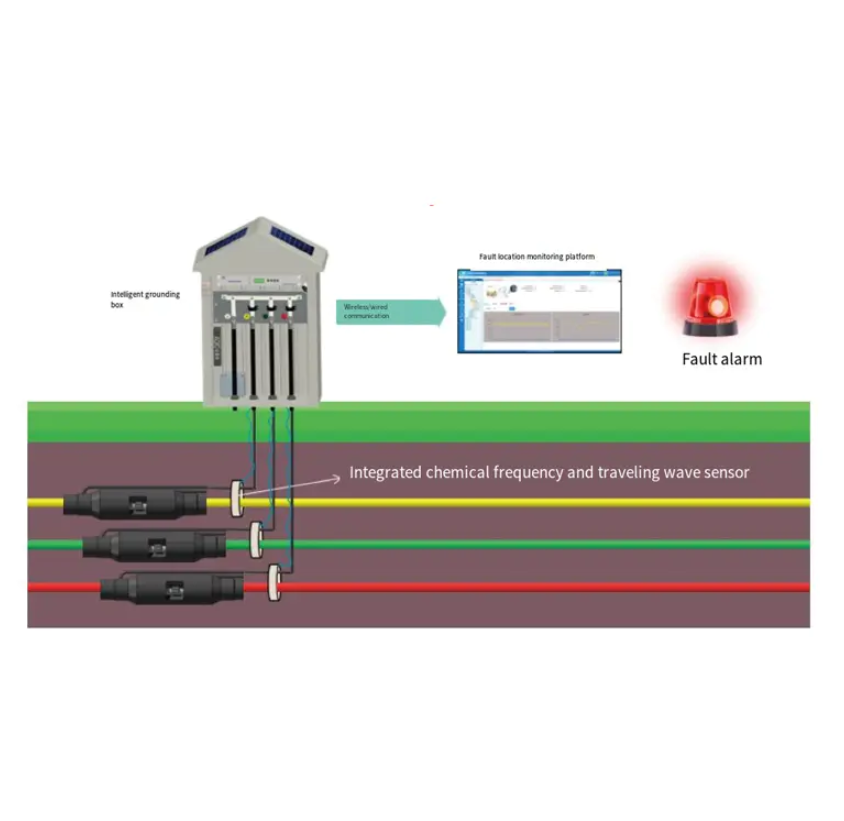
In modern electrical networks, capacitor banks are critical for power factor correction, voltage regulation, and filtering harmonics. Their failure can lead to costly downtime, equipment damage, and power quality issues. An Intelligent Capacitor Online Monitoring System represents a paradigm shift from reactive, schedule-based maintenance to a predictive, condition-based approach. This system integrates sensors, communication hardware, and analytics software to continuously track the health and performance of individual capacitor units or entire banks in real-time, transforming them from passive components into intelligent assets within the broader smart grid infrastructure.
Core Monitoring Parameters and Sensing Technology
The intelligence of the system stems from its ability to measure and analyze key physical and electrical parameters. The most critical monitored metrics include:
- Capacitance Value: Drift from the nominal value indicates dielectric degradation, a primary failure precursor.
- Internal Temperature/Overtemperature: Measured via embedded sensors or infrared monitoring, signaling overcurrent, harmonic overload, or cooling issues.
- Voltage and Current (Fundamental & Harmonic): Monitors for overvoltage stress, current imbalances between phases, and the presence of damaging harmonic currents that cause excessive heating.
- Case Deformation/Pressure: Some systems use pressure or strain sensors to detect internal gassing, a sign of insulation breakdown.
- Ambient Conditions: Temperature and humidity data provide context for the operational readings.
Data Architecture, Communication, and Analytics
The raw sensor data is processed locally by a data acquisition unit (DAU) installed at the capacitor bank. This unit performs initial analysis, such as calculating capacitance from voltage and current waveforms. It then transmits this processed information via industrial communication protocols (like Modbus, DNP3) or wireless IoT networks (like LoRaWAN, cellular) to a central software platform. This platform, which may be a standalone system or integrated into a broader SCADA/DMS (Distribution Management System), uses advanced analytics and machine learning algorithms to establish baseline performance, identify trends, and detect anomalies. It can generate alerts based on configurable thresholds or predictive models that signal the need for maintenance long before a catastrophic failure.
Operational Benefits and Strategic Value
The implementation of such a system delivers tangible returns across several dimensions:
Predictive Maintenance: Enables maintenance to be planned based on actual condition, preventing unexpected failures and extending asset life.
Enhanced Reliability: By preventing capacitor outages, it maintains optimal power factor and voltage stability, improving overall network reliability and power quality for end-users.
Safety and Risk Mitigation: Early detection of faults like internal gassing can prevent case rupture or fire, protecting personnel and adjacent equipment.
Operational Optimization: Data on power factor and harmonic levels can inform automated or manual switching strategies to maximize efficiency and compliance with utility regulations.
Reduced Operational Expenditure: It eliminates unnecessary periodic manual inspections and testing, reducing labor costs and associated safety risks from working on live equipment.
Integration and the Future Smart Grid
An Intelligent Capacitor Online Monitoring System is not an isolated solution; it is a key component of the digitalization of electrical substations and industrial power systems. Its data feeds into asset health dashboards, enterprise asset management (EAM) systems, and ultimately supports the dynamic control needs of grids with high renewable penetration. By providing a continuous, data-driven understanding of capacitor health, it empowers utilities and industrial facility managers to move beyond traditional time-based maintenance calendars, fostering a more resilient, efficient, and intelligent electrical infrastructure.
- Art
- Causes
- Crafts
- Dance
- Drinks
- Film
- Fitness
- Food
- Spiele
- Gardening
- Health
- Home
- Literature
- Music
- Networking
- Other
- Party
- Religion
- Shopping
- Sports
- Theater
- Wellness


